Fall 2019
Edited by Nicholas Pevzner & Stephanie Carlisle
Infrastructure is always political, and energy transitions have always been contested, pitting established players against upstart technologies and new coalitions. How can a radical reimagining of energy infrastructure create opportunities for an inclusive and participatory conversation about climate change and social justice? Who has the power to talk about infrastructure, and who gets left out?
Introduction: Power

Community Power As Provocation: Local Control For Resilience And Equity

Our Energy For Our Country
Speculative Designs For Energy Democracy

The TVA, Fuzzy Spaces Of Power, And Other Purposes

The Missouri River Basin: Water, Power, Decolonization, And Design

Power Plant Power

Arctic Present: The Case Of Teriberka

Coal Ash Wastescapes: The Byproduct Of Our Coal-Fired Power Dependency
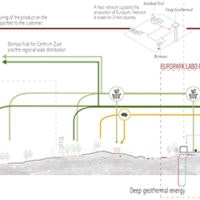
Biomass For All: Designing An Inclusive Biomass Infrastructure

China’s Giant Transmission Grid Could Be The Key To Cutting Climate Emissions

2050 – An Energetic Odyssey: Persuasion By Collective Immersion

The Blue Lagoon: From Waste Commons To Landscape Commodity
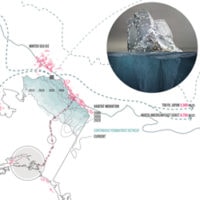
Territory Of Extraction: The Crude North

Daylighting Conflict: Board Games As Decision-Making Tools
Sign Up
Find out more about Scenario Journal and get advance updates and news from the team. Sign up here.→